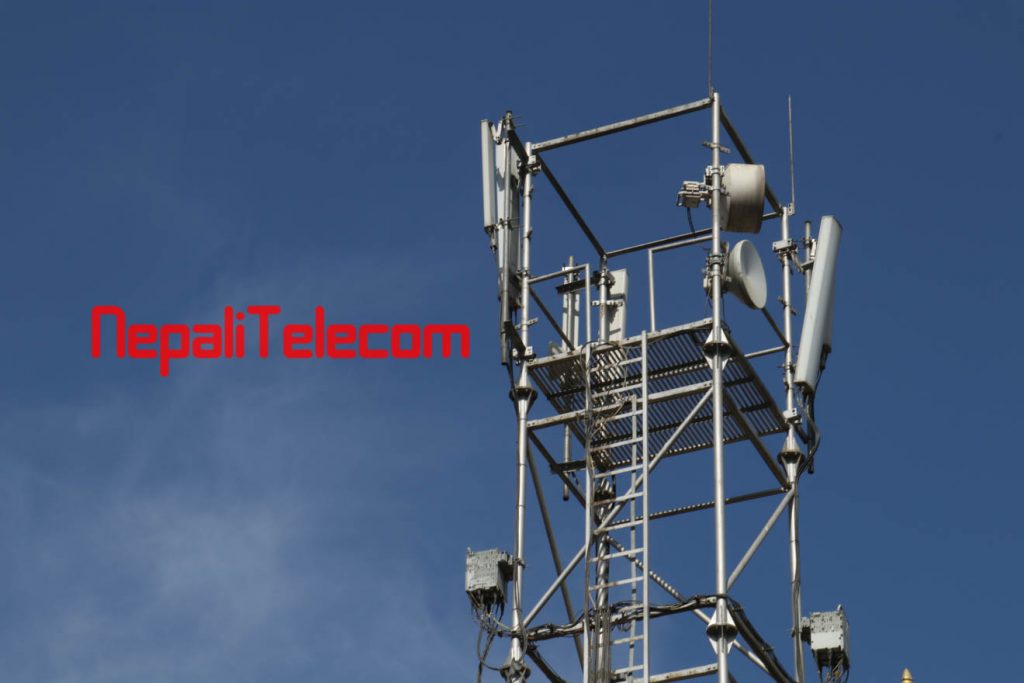
Nepal Telecommunication Authority is known to make the infrastructure sharing mandatory among the telecom operators. As the infrastructure development with telcos is time consuming, costly and has direct impact on the services, NTA has come up with this provision for infrastructure sharing in new regulations.
NTA have already formulated a new regulation called Infrastructure company & sharing rule (Niyimawali) and send it to cabinet for approval. This new rule will make sharing a mandatory requirement for newly made big infrastructures.
How infrastructure sharing benefits customers?
Infrastructure sharing refers to the sharing of mobile towers, powers, shelters and more, among two or more telecom companies with mutual sharing conditions. Telecom infrastructure sharing enables
- cost saving and fast telecom roll-outs,
- invest more on telecom equipment (sites) than civil infrastructure,
- increase quality of service and promote healthy competition among telecom operators.
- And ultimately results in affordable and high quality of service to the customers.

Till now, operators have been building infrastructures individually for their own use and service expansion. It is obvious due to the absence of any such rules. The duplication in infrastructure investment, leased contracts had major impacts on the service expansion and the high cost. Though this sharing had been in the light from several years, it was not finalized and approved.
Infrastructure development after the new regulation.
Now, after the approval of the new rule, telecom operators need to develop infrastructures enough for three operators (to share later). The design and quality of infrastructure need to be as per the regulator’s approval. Due to which, the duplication of investment will end, permitting fast and low-cost expansion of telecom services in several remote and city areas. Which will result in reduction of the cost of the several telecom services for customers and improving the service availability / quality.
The huge infrastructures in telecom sectors are mainly towers of height greater than 7 meters and optical fiber transmission links. The type of infrastructure sharing is passive infrastructure sharing which is for non-electronic infrastructure in cell sites. There is another type of sharing called active infrastructure sharing. Active sharing permits the share of electronic infrastructure like Base stations, Antennas, Transceivers, Microwave and even spectrum.
As there are 6 telecom operators, 42 Internet Service Providers, 85 television channels, 652 FM station license holders in Nepal, the infrastructure sharing is beneficial for all the communication service providers including telecom companies.