- Well, you must have heard of the different generations of mobile networks 2G, 3G, 4G..
- Some people even get confused with the terms..
- 2G, the second generation of mobile networks is mostly available, but 3G, 4G coverage is still not available in all the areas..
Well, you must have heard of the different generations of mobile networks 2G, 3G, 4G. Some people even get confused with the terms. 2G, the second generation of mobile networks is mostly available, but 3G, 4G coverage is still not available in all the areas. Data using customers now prefer 4G, 5G which has faster data speed compared to 2G. Currently, 5G network is growing in many countries but still not available ubiquitously. This post explains 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G mobile networks in simple terms in 2026. We begin from 1G and then end in 5G for the basic introduction.
Table of contents
1G
The mobile technology started from 1G, the first-generation analog mobile having voice call only. There was no data service in 1G.
2G
After some technological advancement, in the early 1990s, the world got to see 2G, the first digital mobile standard. 2G has voice, SMS, and slow data service, whereas GPRS and EDGE’s addition enhanced the speed to some extent. Remember G and E sign on the top, which means GPRS and EDGE. GPRS and EDGE also add Multimedia messaging service, aka MMS.
3G
3G came in early 2000, which can provide voice, video call, and fast data. With several additions of technology, 3G can even offer up to 42 Mbps speed. But a customer gets around 4 to 7 Mbps on average. You can see either 3G or H or H+ sign for 3G.
4G
Lastly, the fastest available speed from a commercial network is 4G in 2009. Which can provide data speed up to 100 Mbps, but it depends on several other factors. Customers using 4G can get data rates from 10 to 15 Mbps on average. You also cannot get the regular voice calls in 4G, so the calls happen from 2G, 3G, or need to add VoLTE (Voice over LTE). You can see 4G or LTE sign in the top for 4G.
Check out: VoLTE in Ntc; Process to activate
5G
5G has started to roll out in the world from year 2019 and still takes few years to become widely available to more areas. 5G provides ultra-high-speed internet (eMBB), ultra reliable low latency communication (URLLC) and massive internet of things (IoT) solution via mMTC. The technology has now become mature with new standards including the Standalone architecture (SA). Various new use cases and business models have appeared to augment the 5G growth in the world. Also read: What is 5G and its services, applications?
Comparison of 1G to 5G mobile technologies
Here is a table for the comparison of all generation mobile technologies.
| S.N | Mobile Technologies | Launch Year | Services | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1G | 1980s | Voice only | NA |
| 2 | 2G | 1990s | Voice, SMS, MMS and slow data | 100 kbps to 300 kbps |
| 3 | 3G | 2000s | Voice, Video call, MMS, faster data | 2 Mbps to 21 Mbps |
| 4 | 4G | 2010s | All fast data and more multimedia services | 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps |
| 5 | 5G | 2020s | Fastest data, low latency services | 10 Gbps |
In the table above, we saw that every decade there is a new generation or new standard for mobile network. 5G currently seems to be the greatest technology in cellular networks which will obviously be dwarfed by 6G (to be available in 2030s).
Which technology to select from 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G mobile network?
If you use voice calls only from you’re mobile, then 2G is enough for you. But in case you prefer data on mobile, then you can either use 3G or 4G technology. As we see the higher speed and more services above, you can always see 4G to be better than 3G. Do read: 3G vs 4G mobile network: Which network should you use?
Generally, if your phone supports a new technology or you can afford to buy a new phone, and the coverage is available in your place, you need to use the latest technology. For now, 5G is not available in Nepal and the latest mobile technology available is 4G LTE. Do read more details and the status of 5G network in Nepal.
For example: if you are in a place where 4G is available, and your phone support 4G, it is better to put your phone in the 4G preferred mode. Considering the high speed, better experience, battery efficiency and service, prefer the highest generation technology (like 4G/5G is its available). But if you have an old SIM card, you also need to change your SIM card and subscribe to 4G accordingly.
Also read: How to activate 4G and use in Ntc, Ncell.
Technologies for 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G mobile
The name of technologies for 2G, 3G, and 4G are:
- 2G: GSM or CDMA
- 3G: WCDMA or EVDO
- 4G: LTE
- 5G: NR (New Radio)
To select a phone in a different mode, For Android, you can go to the
- Settings-> Wireless or mobile networks ->Preferred network type -> put LTE / WCDMA / GSM mode (Automatic mode) or LTE preferred mode or select one of the technology.
Similarly, in iOS, you need to go to
- Settings-> Mobile data ->Mobile data option-> Voice and Data -> Select 4G preferred, or 4G, 3G or 2G on it.

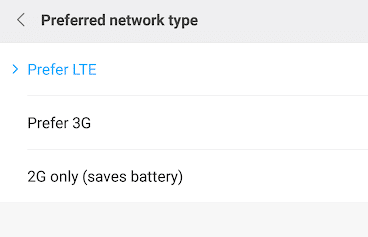
As 5G network is still not available in Nepal commercially, we have provided the screenshot to select the 4G preferred mode in both Android and iOS. However, Nepal telecom was performing 5G trials internally but did not bring it to public trails as only handful of handsets supported it. Check out: 5G NSA Vs SA Architecture
Both operating systems (OS) warns people of more battery consumption with higher speed in 3G or 4G. iOS says, “Using higher mobile speeds loads data faster but may decrease battery life.” Similarly, Android puts save battery in 2G only mode.
We still find people using bar phones or feature phones, which only make calls with 2G networks. Those people will always remain in 2G, but people with faster data preference need to opt 4G/5G if available.
We suggest you read: Why do three mobile technologies co-exist?
If you have any questions about 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and other mobile technologies, please feel free to put in the comment section below.