It’s 2020 and smartphones have been as common as candy. Small to old, everyone uses a smartphone nowadays. It has been a culture to do so. From photography to gaming or doing any other work, smartphones can assist you in various ways. It has been a necessity for people to have a smartphone. Every people use smartphones but not everyone knows about their phone’s specifications. People even buy phones randomly and some pay over price because of a lack of knowledge on smartphone specifications. Put on the seatbelt because, in this ultimate smartphone specification guide ride, we are going to talk about how to read the phone specs.
To make things simple let’s classify the smartphone specification guide into two types: Hardware and Software. The hardware consists of Build, Display, Camera, Processor, Chipset, GPU, Battery, RAM, Storage, and Connectivity. The software consists of an Operating System, User Interface, and Wireless connectivity.
Do Check-Out: OnePlus Nord Launched with 5G And Snapdragon 765G
The Ultimate Smartphone Specification Guide
Smartphone Specification Guide: Hardware
Build

First on our list of smartphone specification guide is about Build quality. Every smartphone is built differently resulting in durability. Frame, Glass Protection, and certification are important things regarding build. Frames are built from Plastic, Aluminum, Steel, and Metal. It all depends upon the price range.
Glass Protection is an additional layer of special glass that is added on both the front and back of the device. There is much Glass protection but the most famous is the Corning Gorilla Glass. It comes in many forms and is classified from 1 to 6 numbers. Next is certification, which proves the phone is safe against water, splash, sweat, or dust. It is referred to as IP certification. For an average user Plastic frame, Corning Gorilla Glass 3 with no IP certification or low-level certification would be enough.
The flagship Samsung phones have IP ratings of IP68 where the first digit is for dust and second is for water resistance. So, 68 refers to dust-tight and water-resistant above 1-meter immersion.
Display
Without Display, a smartphone isn’t a smartphone. It’s the first and last thing that makes a smartphone. There are countless types of display and are also classified. Popular display types are IPS LCD, AMOLED, OLED, Super AMOLED. Nowadays, they all house Water-drop notch, punch-hole, or other cutouts that houses the front camera. In terms of power efficiency and better viewing, the AMOLED display is what we should prefer, and the time has come even the entry-level devices will come with it.
Some of them even come with the in-display fingerprint scanner. Which means the finger-print scanner is inside the display. The displays have resolution such as HD, FHD+ and list go on. An average user would be cool with an IPS LCD FHD+ display. But if you like watching content or gaming than Super AMOLED would do the job right.
Now let’s talk about the screen-to-body ratio. It is basically telling how much of the display covers while compared to the whole body of the device. If the screen-to-body ratio of a device is 80% then it means 80% of the device’s surface is a screen and the rest of the % are other physical parts that wrap the device. A 73% screen-to-body ratio will be enough for an average user. Whereas 88% or higher is necessary for good gaming performance and multimedia watching.

Having a pop-up camera can also increase this screen to body ratio for an immersive experience. Though people are found to be worried about the mechanical motor in such pop-up camera, they happen to perform better than people’s expectations.
Cutouts on display have become a modern trend. It is used to achieve a more screen-to-body ratio while accommodating a selfie shooter. They are often referred to as Notch and Punch-hole. There is the traditional display with no cutouts basically thick bezels just like iPhone SE 2. Then there are modern cutouts which are Wide notch, Water-drop notch, Pill-shaped punch-hole, and single punch-hole. Punch-holes are the real thing.
The latest offering in the display is the higher refresh rate which enhances the smartphone viewing experience and puts a lesser strain on your eyes. Normally, the screen refresh rate is 60Hz which is now increased to 90Hz and some even have 120Hz. The high-end phones like S20 series, OP8 Pro offer 120 Hz display while the Mi 10 and Realme 6 offers a 90 Hz display.
Camera
Now here comes one of the most important parts. The camera is always the talking point when a smartphone launches. There are 3 elements in a camera which are light object (lens/sensors), chemical object (film), and mechanical (camera body itself). Camera sensors are basically measured by MegaPixel (MP) and it is also numbered by the no of pixels in an image or the sensor of a camera. In the camera sensor’s case, the higher number doesn’t always beat the lower one. The MP in a camera ranges from 8 MP to 108 MP. Other specifications in the camera such as Aperture, ISO levels, pixel size, no of camera elements, and others are also important.
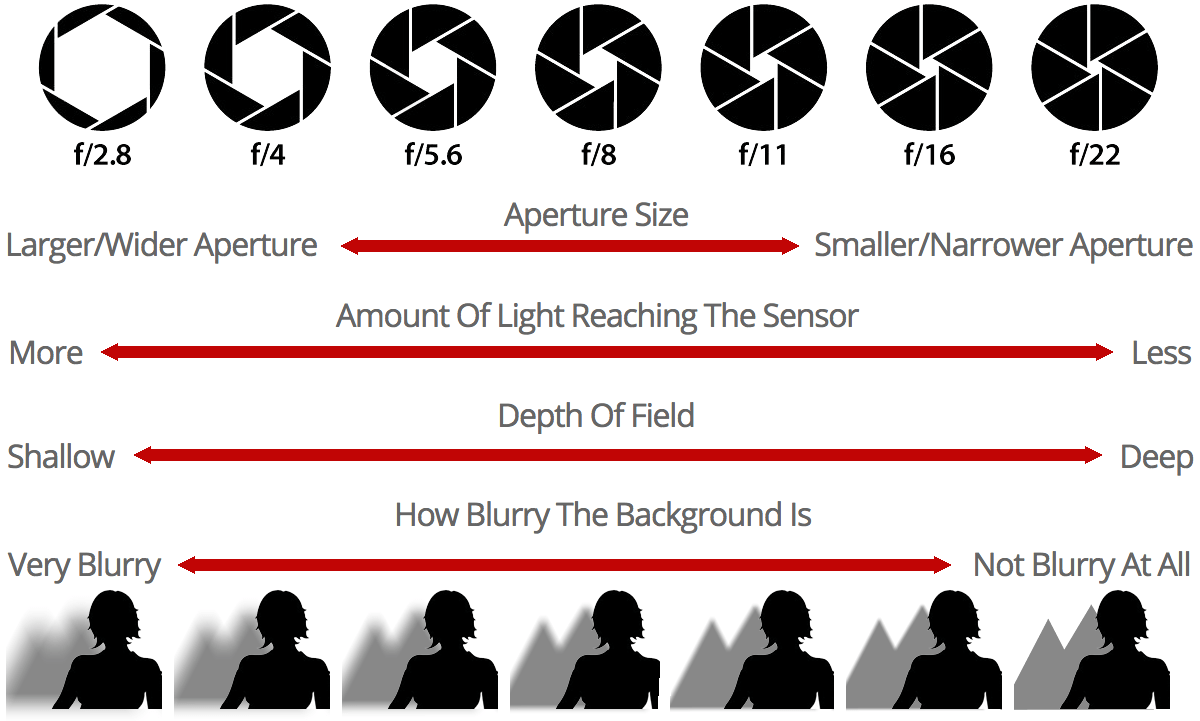
Aperture is the size of the opening that controls the amount of light that reaches the lens. Lower the F stop (aperture) number, the larger will be the opening. F/1.7 has more big opening and passes more light than F/2.0. Similarly, the lower F stop also provides a shallower depth of field.
ISO refers to the sensitivity of the camera to the light. The more the value, the higher will be the light-sensing capability of the camera. But if it’s too high, the image produced will be quite grainy.
Now you’ve about the camera sensors and let’s learn about the types. Currently, there is 4 famous type of camera sensors featured on a phone. Primary sensor, Ultra-wide sensor for wider photos, Macro sensor for small object photography, and Depth sensor for portraits. There are also camera setups such as Dual, Triple, and Quad or more. Basically, the number of camera sensors used in a camera setup defines the whole. Dual means two camera sensors and Quad means a four-camera sensor, it goes on.
Phone cameras also have zooming capability with optical zoom and digital zoom. Some of the phones also offer hybrid zoom that takes into account of both optical and digital zoom. Huawei phones are the front runners in this camera zooming function where they inbuilt 10X optical zoom, with Huawei P40 Pro. Samsung S20 Ultra, Mi 10
Camera Setup, Modes, and Video Recording
Nowadays, Dual camera setup at the front and Quad camera setup at the rear has been normal. For an average user, a single camera sensor at the front and Low MP Quad Camera Setup will be more than enough because even budget phones are nowadays coming with a quad-camera setup.
For making fine of such a camera setup, the software part plays a vital role. Yes, I mean all the modes and features that you find on your smartphone. PRO Mode, Night Mode, Panorama, HDR+ feature, Auto Focus feature, Portrait mode, and so on. If you are going to buy a new phone then probably you will get this all mode even in budget phones.
Not only these modes are important for snaping good images but other factors are also important. Object detection and image stabilization are few of the factors. Optical image stabilization and Electronic image stabilization (OIS/EIS) are image stabilization technology used in smartphones which makes the phone shoot sharp even while moving. Object detection detects objects in an environment using machine learning to take better photos, idle for that object.
Video recording is also important. Smartphones nowadays can record even up to 4K resolution. Recording videos in 4K at 30fps is for content makers but for average user recording videos in 1080p at 60fps will be enough. Slow-mo, Hyper-lapse, and others are video recording types that are commonly found in every smartphone nowadays.
These days, some of the phones support the RAW shooting that will capture all the details of the camera sensor in raw format. Normally the file size of the RAW capture is quite high like that of the DSLR. If you are one of those who prefer post-processing photos later, you may look for this feature.
Processor
The processor is the heart of the smartphone. It is what determines your phone performance. A processor’s working rate is measured by its number of cores and the clock speed usually mentioned as GHz. There are Dual-core, Quad-Core, and Octa-core are normally found on smartphones nowadays with an average 2.0 GHz.
Higher the cores and the clock speed, the better it is. Octa-core with 1.8Ghz will be enough for an average user to just surf on social media smoothly. Octa-core with 2.2Ghz or higher will be good for gamers and heavy task doers.
Chipset
The must-know thing on our smartphone specification guide is about chipset. Chipset is another component that determines the performance delivery of the smartphone. It is an integrated circuit that combines all basic components of a computer system in one chip. That’s awesome. There are many chipsets out on the market and many smartphone manufacturers build their own chipsets.
Such as Samsung built Exynos series, Huawei built Kirin, Apple built A Bionic. MediaTek also does a fine job but the one that stands at the top is Qualcomm’s Snapdragon series. They are also labeled by numbers and the rule is the same. A higher number means higher performance delivery and quality.

They have their own entry-level, mid-range, and high-end processor SoC. Regarding the Qualcomm processor, the SD400 series is for the entry-level processor for affordable devices. Similarly, SD 600 series and SD 700 series are the SoC for average mid-range and upper mid-range devices. While the 800 series in Qualcomm is for the high-end flagship phones. The latest SD865 SoC powers devices like Samsung S20, OnePlus 8 Pro, Mi 10 5G, etc.
GPU
GPU is basically Graphics Processing Unit that is responsible for all high graphics works, gaming, and even high-resolution video watching. Without this component, the smartphone can’t deliver any gaming performance or device’s visual output. AR emojis or anything related to AR wouldn’t have been possible without GPUs. Mostly only two GPUs are commonly found which are Adreno series and Mali series. They are also numbered and a higher number label means higher performance.
Adreno 540 GPU is enough for average users whereas heavy gamers will need Adreno 618 for smooth and lag-free gameplay. For Mali GPU, Mali G31 is good for average use. For heavy gamers, Mali G75 will do the work.
Battery
To operate a smartphone, you will need a source that provides a device with the required energy right. The battery is that source. Without the battery, the smartphone is just like a dead body, and giving it life is a battery. They come in various sizes determined by mAh. Fast charging support and other features are additional features that come with the battery nowadays.
For an average user, a 4000mAh battery will be enough. But in today’s world where social media apps and others use way more energy than previously. Getting a 4500mAh battery (Similar to Poco X2) will be beneficial. As for Gamers, a 5000mAh battery is a must because the usage is very high. Going for a 6000mAh battery (Similar to Galaxy M31s) would be better.
You can also improve battery efficiency. Enable Dark Mode, Dimming the display, Putting on Power saving mode, closing unused apps, and stopping unnecessary motion features can improve the battery’s efficiency.
RAM
RAM is responsible for making all the applications in a device work and also for multitasking. Operating system to games to normal random applications, every app needs a bit of memory that RAM provides. Having more RAM helps to run more applications at once and smoothly. RAMs also have types like LPDDR2, LPDDR3, LPDDR4, and so on. Getting a smartphone with LPDDR4 2GB RAM will be enough for an average user. Apps will run smoothly if not executed heavy tasks.
Whereas for Gaming and huge multitasking, you need to have more than 6GB of RAM. These days, the flagships phone integrate higher than 8 GB of RAM. It’s not only the RAM size and the generation but the better RAM optimization can lead to provide higher-end performance and smoothness.
Storage/ROM
Storage is a big aspect because it is where a user keeps all of this data, files, and other stuff on a smartphone. Even the software and apps are installed here. Storage is basically a memory where all of your taken photos, downloaded stuff, and another type of file are kept. It is also accessible right away.
Nowadays, 32GB of storage is commonly used because there is an option to expand storage via an external microSD card slot. Most people directly keep their files in the cloud-based system which is regularly synced. So, for an average user, getting a 32GB storage with an expandable option would be best.
All those who do not prefer to sync your multimedia to the cloud and take a lot of photos every day, I would recommend checking 128GB of storage and the expansion SD Slot.
Connectivity
Last but not least no our smartphone specification guide on hardware is connectivity. Connectivity basically includes the Network that the smartphone supports, all the sensors, ports, and connectors to Wireless connectivity such as Wireless charging and Reverse charging.

For Mobile network support, the latest smartphones are coming with 5G Network but not everyone. The 4G network is still evergreen as it should be and will be till 5G is ubiquitous at all places. For a fast reliable internet on the go, the 4G network is enough whereas some use the 3G network only due to no 4G support in their phone. But as we compare 3G vs 4G, 4G is better in every aspect to use the 4G network. While buying a 4G phone, you need to check if the phone supports the spectrum bands from the telcos in Nepal, like Band 3 and Band 20 of Nepal Telecom.
Similarly, for more features in 4G, look out for VoLTE voice over LTE calling and VoWiFi (Voice over WiFi) if the network in your area supports it.
As for sensors, phones commonly have a Finger-print mount, Gyroscope (for orientation), Accelerometer (for motion/vibration), and various others. Similarly, there are ports like 3.5mm headphone jack connector, micro USB or Type-C connector for charging SIM slots, and microSD card slot.
For an average user, every port will be necessary along with all the sensors. As for NFC, Wireless charging support, and Reverse charging, you won’t need it if you are an average user.
Smartphone Specification Guide: Extra Bonus
There is also an in-display fingerprint sensor and Face unlock sensor. The in-display fingerprint sensor is a fingerprint sensor placed beneath the display. Face unlock sensor is basically found along with selfie shooter but sometimes with the use of software selfie shooters themselves can do the work of a face unlock sensor.
Fast charging is a technology that helps your battery to charge at a fast speed. For example, 25W Fast charger can charge an average battery from 0% to 50% in 30mins. The best one is VOOC technology by Oppo which is also used by OnePlus as Dash Charge. Read about Oppo’s latest 125W Super VOOC charger.
Wireless charging is basically a feature that lets you charge your phone wirelessly. Reverse charging is a feature that can turn your device into a power bank and charge another device wirelessly which also should support reverse charging. For an average user, all these features shouldn’t matter. But if you want to live a modern life, you should care to have one.
Do, Check-Out: Oppo Enco W31, W11, and M31 Launched in Nepal
Smartphone Specification Guide: Software
OS
One of the main things in this smartphone specification guide is about OS. OS is an Operating system that makes all the hardware of the phone run. It gives life and guides the hardware to run like it is supposed to. There are many Operating systems made for smartphones such as Android, iOS, and others. But these two are the conquers of all. Android is of Google which is used in almost smartphones whereas iOS of Apple and are only used in iPhones. Each of them has its own benefits.

Android 10 is the latest version for Google OS whereas iOS 13 is the latest version for Apple. Android is customizable and flexible whereas iOS is simplified and security centrical. Getting an Android 10 powered phone seems better because it’s quite better than iPhones and the options are countless. But if you worry about security and don’t care about customizing or money than iOS 13 is the one. It depends upon your taste.
Now comes the great question. Which OS is more power efficient? Android consumes 161% more power on average, while iOS consumes 142% more power on average. Therefore, we can see that iOS power efficiency is on average 19.7% better than Android.
When it comes to AI both platforms use the Machine learning Algorithms for boosting the performance and efficiency of the phone. The AI features can also enable the phone to last longer and capture nice photos. Both platforms have first-class support for Machine learning applications and features. You should check whether the phone software supports AI features.
UI
If you want to buy an iOS phone then you can skip this one, because it’s all about Android. UI is the User Interface of a smartphone. UI is nothing but everything that a user can see and interact with a smartphone. The app drawer, home screen, etc are all part of UI. Many manufactures use Android OS but layer it with their own UI. Samsung has OneUI, Vivo has Funtouch, Oppo has ColorOS, Huawei has EMUI and Xiaomi has MIUI. It all depends on the brand you are in. An average user can choose anyone.
But each UI have their own multiple numbers of bloatware. It means pre-installed apps that belong to the manufacturer. UI and bloatware also depend upon whether its Global ROM or Chinese ROM. Global ROM has basically all the Global builds while Chinese ROM only have their traditional. Google stock Android UI has the least bloatware whereas MIUI and Funtouch conquer the large number.
Wireless Connectivity
You may question now; connectivity was already on the smartphone specification guide hardware section but why again in the Software section. Well, that because there is software built for connectivity as well which includes Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, IR, and NFC (Near Field Communication). You should also read if the WiFi band in the phone is of dual-band: 2.4GHz and 5 GHz. There is a new band coming for WiFi called WiFi 6E which will be faster.
Getting a smartphone with Bluetooth 5.0 version, Wi-Fi dual-band with no NFC support shall do the work for an average user. But if you want to use the NFC payment in your place, then do look out for the NFC support. Similarly, with the IR support, you will be able to turn your smartphone into the remote real quick, available with Xiaomi phones.
Smartphone Specification Guide Conclusion
Both the hardware section and software sections are equally important in a smartphone. While reading a smartphone specification, we request our readers to look on both sides. Some phones come with the latest software but not good hardware or just the opposite. So, it is us who should know about all the terms and act smart.
Next time when you are getting a new phone, please do check all the specifications and try to get a Global variant as it is compatible with most of the countries. If you are already looking to buy a phone then check our list on Best Phones Under Rs. 15,000 in Nepal and Best Phones Under Rs. 30,000 in Nepal.













