Learn why your mobile network fluctuates among 2G, 3G, and 4G and how you can avoid it for better voice calls and broadband experience.
Have you experienced mobile network fluctuation on your device? It can be very annoying when it abruptly disrupts your call, streaming, or downloads. This issue is especially common in the outskirts, hills, and rural areas of Nepal. At times the network on our devices switch between networks and at other times we lose the signal totally. It is nothing but a major inconvenience to mobile users.
Network fluctuations are detrimental to our telecom services in general. Despite telecom operators inundating us with different networks, the issue is still there. Now the question is, what could we do for a stable network on our phones for consistent voice calls and broadband internet? Let’s delve into it and explore the solutions. Before we move on, let’s begin with how our mobile networks work in basic.
How Do Data And Calls Work On Mobile Network?
Well first let’s talk about how a mobile network works in layman terms/ When you talk over a phone, the antenna inside your phone connects to the nearest cell tower via the air (radio waves) to the nearest cell tower. That tower then reroutes the data from your mobile to the telco center and then to the receiver you are talking to.
Similarly for data usage, Smartphones exchange packets of digital information with cell phone towers via radio waves. For this, your mobile phone connects to the nearest cell tower from where the data request is forwarded to the telco center for further communication. Then, it connects your phone to the internet and also performs data exchange for calls, SMS, and more.
To improve both voice calls and mobile broadband, next-gen networks were introduced that enhanced both voice calls and data. 2G saw an upgrade to 3G, which was later succeeded by 4G. While 2G operated on GSM technology, 3G ran on WCDMA and 4G on LTE. But despite mobile networks leapfrogging to next-gen technology from each upgrade, the issue of network fluctuation remains while 2G, 3G, 4G mobile networks coexist.
Why Do Mobile Networks Fluctuate?
Mobile network fluctuates for various reasons. From the distance between mobile phones and the cell towers to the physical hazards in-between the mobile phone owners and the cell tower, poor signal strength and even power failure at the cell towers are the reasons which break down the network strength and the network starts switching among 2G, 3G, and 4G. While telecom operators have certainly filled up newer tech and innovations in cellular networks, mobile network fluctuation is still persistent. In fact, it has been an intrinsic issue that has plagued us on mobile at times.
Let’s take each of these common factors and elaborate on them followed by what we can do to abate network fluctuations on our mobile devices.
Multi-Path Propagation
The multiple-path that the signal takes to reach you is also one of the reasons for the network fluctuations. It will be too much technical to explain it in detail. But the mobile network signal (either 2G, 3G, 4G) undergoing multiple paths can have signal canceling results, which reduces the strength even if you live nearby the tower. The environments and mobility play a vital role in multipath propagation. Since either of the technology have different results (due to the different spectrum and technology they are using), the signal degradation might differ prompting your phone to switch among them.
Distance From Cell Towers and Environment
The most immediate reason for mobile network fluctuation is the network strength on your phone from the nearest cell tower. The bars in either corner of your mobile phone represent the signal strength you are receiving from your nearest cell tower. Our phones run on different network standards for different cellular networks such as GSM and CDMA.

The 2G network operates on GSM standard and 3G works on WCDMA, which is the modified version of CDMA (compatible with GSM though). Ideally, a 2G and 3G base station can dissipate its signal beyond more than 30 km of area. If you happen to live in an area far from the cell tower’s ideal coverage, you can expect an inconsistent mobile network to trouble you. Moreover, physical obstructions in-between could bring that coverage number down to as low as 2-3 km at max. Physical barriers such as walls, buildings, hills serve as impediments to better signal strength. Even if you have a cell tower just around, those barriers could bring you limited network strength resulting in network fluctuations.
In sum, distance plays a key factor in determining signal strength from cell towers. The far you are from the base station, the poorer reception of signal resulting in glitchy, and interrupted voice calls. Whereas the environment and terrain (hills and besi) will also affect the signal strength in a particular area.
Nearby Tower Failure
Although cell towers are pre-equipped to handle many issues, power failure among others has been another cause disrupting mobile networks on occasion. In case of a tower failure due to power or transmission or equipment faulty, the mobile might receive a signal from a farther tower, resulting in low signal strength. As the mobile constantly looks for better signal in higher Generation technology, it results in more network fluctuations to the annoyance of phone users.
Due to the backup for power, electricity cut-off is a lesser concern but it also has a backup hours after which, the moble tower goes up with no any battery juice similar to our mobile phone. While transmission, equipment failures also add up to the network fluctuations.
Mobile Network Setting
Another key reason you find your mobile phone oscillating between 2G, 3G, or even 4G network is that you have the mobile network set on automatic mode. This dictates your phone to look for the strongest network available and switches itself without your intervention.
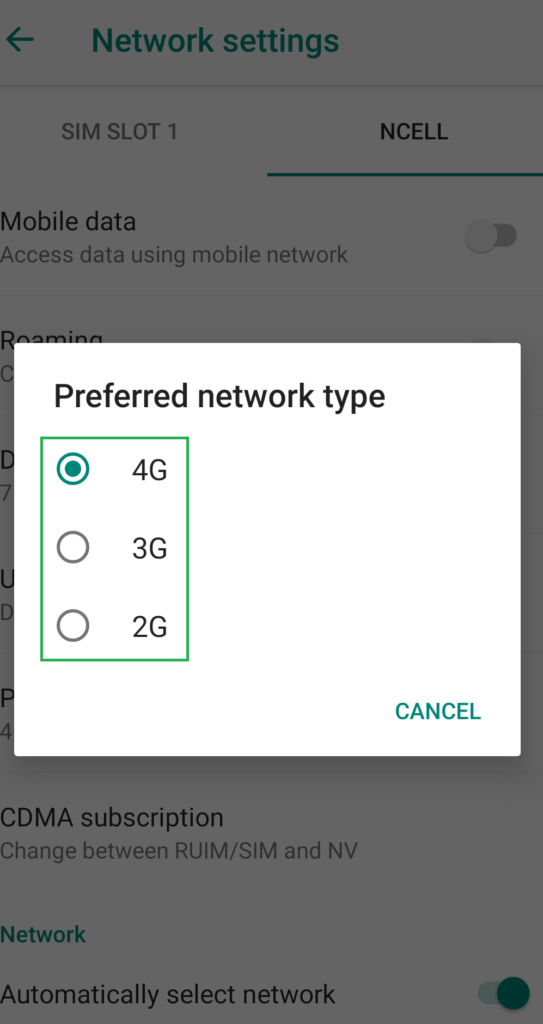
It is possible that your device is on automatic network mode without you realizing it. Smartphones come on this setting by default and formatting phones also restore it back to this setting. So when your device starts operating, it searches for the best network available and makes the switch. Unfortunately, if you are in an area prone to poor network strength, your mobile network will randomly fluctuate.
The problem is if you are on 3G while making a phone call, or browsing the internet and suddenly the network strength drops, the system on your phone decides to switch to another network, likely 2G. The bigger worry is, such a transition is not flawless. If you are on call, you could miss the vital conversation, or lose the call, and for broadband, 2G won’t deliver a good bandwidth experience.
Check out: How to solve Mobile data not working problem?
Lack of 3G and 4G Coverage
While you are moving away from trade centers to the outskirts or remote areas, you may not access 3G and 4G networks. The third-gen and fourth-gen networks are still elusive to many areas in Nepal especially, along the highways, hilly regions, and remote hinterlands. Now if you find yourself in such places, your device will have trouble getting a consistent mobile network. So, you will see recurrent network fluctuation.
Even in cities, 3G and 4G in the higher spectrum bands can not penetrate in some areas. The higher the spectrum bands, the higher will be the loss of signal relative to distance and obstacles. So 3G/4G in higher bands will definitely output low signal strength in such locations. Alleyways, outskirts, large building settlements, basements, or parking lots are subject to more network fluctuations due to higher signal loss. Even in case of nearby tower failure, 2G can reach you with higher signal strength while 3G, 4G struggle to get better strength. In such cases, your device will look for the strongest network strength while prioritizing higher technology (for Auto mode), which results in network switching back and forth between 2G and 3G/4G.
Read: 3G Vs 4G; Which mobile network to use?
Our Suggestions
Recurring mobile network fluctuations can be a painful experience to us especially while we are on something urgent be it a call or a large file download. It could disrupt everything. But, there are certain things we can do to avert it and improve our mobile phone experience.
Below, we have compiled a list of a handful of tips and tweaks which help you avert those disturbing network fluctuations that will bring you peace of mind while on phone.
Manual Setting Might Help You!
Automatic setting on devices is to benefit mobile phone users. It allows them to take advantage of the best network their carriers are providing no matter where they are. But in particular areas, it does the opposite. Not only your device switches back and forth between networks, but it also leads to battery quicker consumption. For those odds, it sometimes may help you by putting your device manually on a particular mobile network.
This is especially beneficial when you are traveling beyond urban centers or along a highway because those areas are prone to low signals. As soon as your phone detects a low signal on your current 4G or 3G, it will try to come down to 2G if available or vice versa. But if you put the phone on one particular network, it will give you better network stability. In cities, you can try setting your device on 3G and 4G for broadband, and in areas beyond, 2G for better voice calls.
But there are times your phone doesn’t receive a good reception while you need its high-speed broadband. In those cases, put your device on either 3G or 4G manually and raise it above. If it catches a signal, then set it there and connect it to a laptop via Hotspot tethering. This way, you can make do with mobile broadband in need.
Having your device on the automatic setting is actually a benefit to phone users. It ensures that you are getting the best mobile network all your day whenever you move. But the issue is, for areas with lower signal reception, it is not ideal. As it not only brings unstable network but speeds up battery drain. However, if you are in trade centers and generally have a good network, you can prefer to stay on automatic mode for the best mobile services.
Confirm The Strongest Network
If mobile network fluctuation is a recurring issue in your place, it is handy to first learn which network serves you best. Therefore, check which network is the strongest in your area. To determine it, go to your phone’s Settings app – About phone – Status – SIM status – Signal Strength. There you will see a number representing the strength of the network.
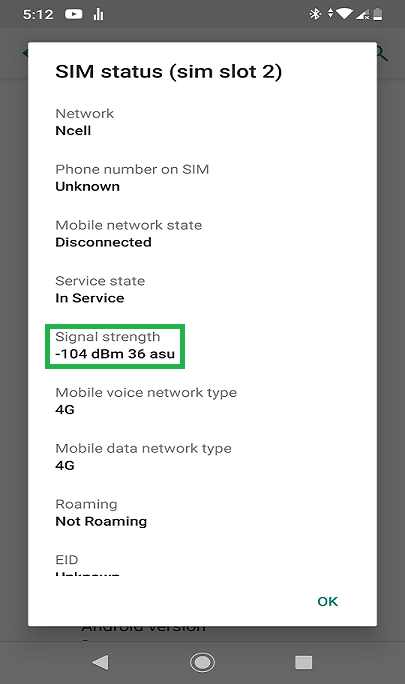
These numbers are in the negative and the lesser number stands for a better signal. Signals lower than -85 decibels are considered strong, and it’s rare to see a better signal than -50 dBm. But remember they do not reflect the strength of 2G, 3G, or 4G, but the network’s strength on your phone. So check which network gives you the lesser number and you can stay assured about that particular network giving you the best performance. Now, you can put your device manually on that network among 2G, 3G, and 4G for a consistent signal.
Check out: Nepal Telecom recommendations for Auto mode for seamless 4G signal
Choose Network As Per Your Priority
It is also important to acquaint us with the usage of each mobile network which helps us utilize each network to our best. 2G succeeded over 1G and remains ideal for voice calls. Meanwhile, its successor third-gen or 3G network was designed for data and voice both on the WCDMA standard. 4G, which is the norm these days is used for data and requires a separate VoLTE technology for voice calls. Meanwhile, the next-gen 5G will also be for ultra-fast broadband and low latency services.
Learning about each of the networks is crucial to receive a more efficient performance from each network. It helps you choose the network that meets our demands best. Depending on the availability, you can select one particular network for the best possible service. If you need voice calls, you can employ a 2G network for this. If you need better data and voice calls, opt for 3G. In case, high-speed broadband is your preference, select 4G.
We also suggest that you put your phone on Auto or 4G/3G/2G that will select the network based on availability. However, if you do not need broadband internet, and can stay content with calls, we suggest staying on 2G as it maximizes your voice calls, saves you from annoying network fluctuations, and also improves your phone’s battery efficiency.
Voice Call On 4G
Have you noticed that when you are on 4G and try to make a call, your device will switch back to either 3G or 2G if it’s on automatic settings? This is because 4G doesn’t support voice calls like traditional calls over 3G, 2G. Chances are when your mobile move to 2G/3G for voice calls, it could not come back to 4G immediately, giving you less internet speed. However, NTC has launched its VoLTE service that works on 4G and allows users to perform HD voice calls while also using data simultaneously. Meanwhile, 3G natively supports high-speed data and voice calls, the video call with 3G is almost extinct.
Conclusion
In this post, we briefed about mobile network fluctuations and solutions to minimize them. We also relayed some tips that you can take up while moving away from urban settlements to the outskirts and remote areas.
In all, people use 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks for their different characteristics and purposes. If you need high-speed broadband and voice calls, you can choose 4G with VoLTE or 3G. But in case you need voice calls only, put your device on 2G. Manually setting your device would need you to switch between networks for higher broadband performance, for eg. from 2G to 3G or above. But in case your area has a good network reception, you can easily set your device on an automatic network that will serve your all needs without you bothering.
For more: 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G explained in simple terms
Do you also face network fluctuations on your phone? If you do, the above tips and tweaks may help you avoid such nuisance and get a stable network on your device. If you have anything to add to it, let us know in the comments below.












