Samsung Electronics, the world’s leading semiconductor has successfully demonstrated the world’s first in-memory computing based on MRAM. This breakthrough technology merges data in memory and not on a separate disk thus improving power efficiency. The tech giant has published its paper on Nature.
The test highlights Samsung’s growing lead in-memory technology which will prove pivotal for the next-gen AI chips’ advances.
Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology and Samsung Electronics Foundry Business and Semiconductor R & D Center collaborated for this research.
Merging memory with a system chip has received years of study and trials. But Samsung has achieved a breakthrough.
Related: Samsung Unveils Second Generation 5G Chipset For Network Equipment
What is In-Memory Computing Anyway?
In-memory computing is the next-gen architecture in Memory technology. This runs differently from the current one and could translate into huge power efficiency in upcoming devices in the future.
In the conventional memory system, the data is stored in memory chips meanwhile, data processing takes place in separate chips.
But in in-memory computing, both data storage and computing merge in a memory network. Thus this architecture can process a large amount of data without moving the data. This means power consumption reduces in devices.
Power efficiency has been a focal key point in the current generation of devices. As in-memory computing can bring a breakthrough for the purpose. That is why it has emerged as one highly sought-after technology in-memory network.
Also read: Samsung Develops 8nm RF Solutions For 5G Chip
Samsung’s Breakthrough Comes with MRAM
What is even more interesting is Samsung’s in-memory computing achievement comes with MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory). For years, developers have used Non-Volatile memories – PRAM (Phase-change Random Access Memory) and RRAM (Resistive Random Access Memory) for in-memory computing. But using MRAM proved difficult for this purpose. It is because it has a low-resistance characteristic that obscures its power reduction advantage.
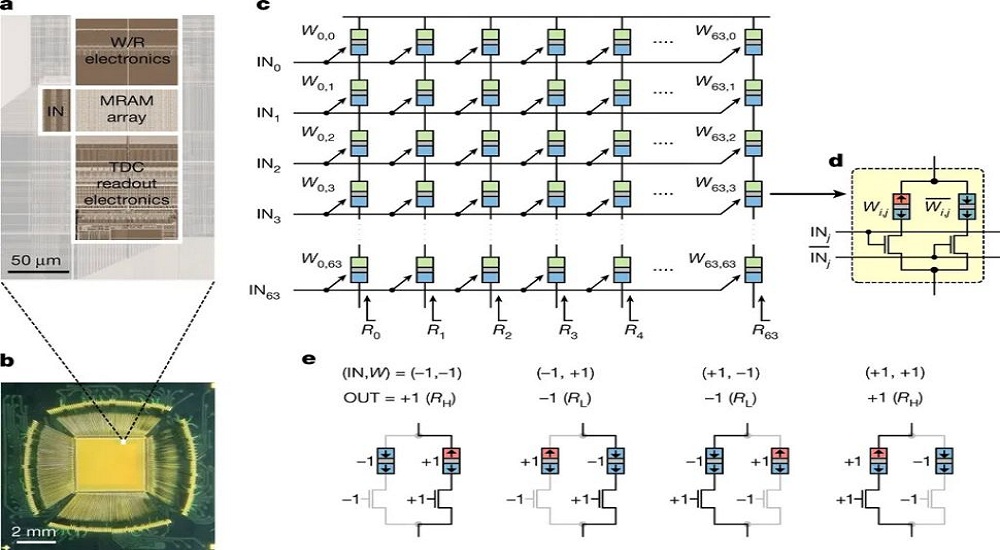
Samsung found a solution to it with its architectural innovation. Their research team built an MRAM chip replacing the traditional ‘current sum’ architecture with ‘resistance sum’ and ran the demo in a 64 × 64 crossbar array based on MRAM cells. This addressed the problem of resistance on MRAM devices.
In its test, Samsung achieved “98% of accuracy in classification of hand-written digits and a 93% accuracy in detecting faces from scenes.” This breakthrough could potentially transform the next-gen AI chip technologies.
Check out: Samsung Mobile Price in Nepal | Latest Update
More Than Just a Memory Technology
Dr. Seungchul Jung, the first author of the paper says, “In-memory computing draws similarity to the brain in the sense that in the brain, computing also occurs within the network of biological memories, or synapses, the points where neurons touch one another.”
“In fact, while the computing performed by our MRAM network, for now, has a different purpose from the computing performed by the brain, such solid-state memory network may in the future be used as a platform to mimic the brain by modeling the brain’s synapse connectivity,” he added.

Moreover, Samsung’s innovative MRAM technology can also be used to download biological neuronal networks. The researchers say, “In-memory computing draws similarity to the brain in the sense that in the brain, computing also occurs within the network of biological memories, or synapses, the points where neurons touch one another.”
Check out: Exynos 2200 delayed, S22 series might only come with SD 8 Gen 1 instead
Samsung’s In-Memory computing is still in the development phase and its entry into the consumer market could still be a few years ahead. But Samsung has claimed the frontier and will take it as a reference for its leadership in in-memory technology for the future laptops, smartphones, and other devices.
The in-memory computing will allow data storage in RAM rather than on Hard Disks. This could transform the way electronic gadgets work in the future for good. How excited are you with this news? Do share with us in the comments below.