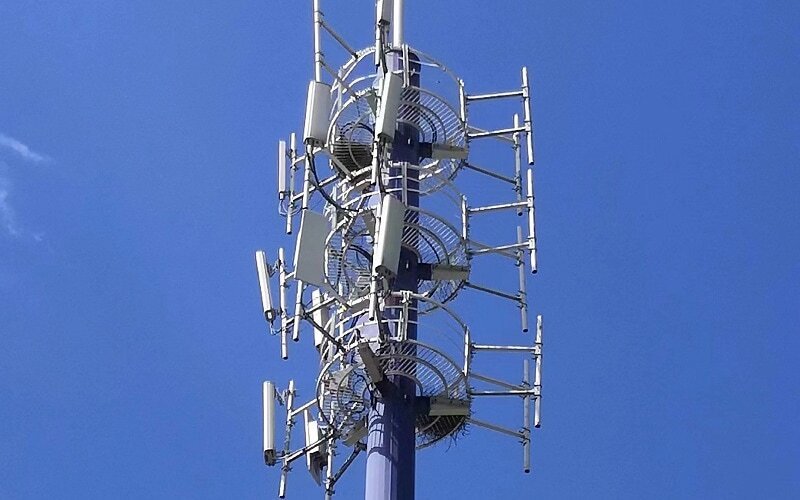
Chinese telecom giant China Unicom has collaborated with Huawei to complete over 1,000 network sites MetaAAU deployment in Beijing. This marks the first remarkable step in the Gigabit Green Village strategy.
Both China Unicom and Huawei have commercialized MetaAAU at over 1,000 sites. This has formed the world’s largest ever commercial MetaAAU network. This is vital to unlocking the growing mobile subscribers’ demand for 5G traffic in rural settlements. In the meantime, this will also increase 38% of total traffic in a single site.
MetaAAU is a significant upgrade over the previous generation AAUs. The MetaAAU lessens site energy usage by 5% under the same workload. It is vital for energy efficiency. Similarly, MetaAAU’s deployment serves as an important step toward the green and digital village ambitions for the 5G Capital Project.
Do read: 3 Ways to Build Sustainable and Digital Asia-Pacific
MetaAAU and its features
MetaAAU is the third-generation AAU developed by Huawei. The advanced MetaAAU utilizes a new architecture – an extreme-large antenna array (ELAA). This doubles the array scale in comparison to the previous AAU architecture. This leads to an extended coverage as channel beams are narrower in it and energy is more stressed.
With innovative algorithms, the MetaAAU enhances network efficiency while also reducing energy restraint. Expectedly, this benefits China Unicom’s Beijing requirements for 5G constructions in towns and rural areas for 2022. The project comprises large inter-site distances, gigabit user experience, and green networks.
In July this year (2022), China Unicom Beijing deployed MetaAAUs at over 1,000 sites in both towns and rural areas in Shunyi, Huairou, and Pinggu districts. They are successfully in commercial markets now.
Since its development, MetaAAU has increased user traffic by 38% in these areas. Besides, it covered 37% more users and brought a 40% wider coverage area.
Additionally, the MetaAAU also resulted in 10% higher uplink and downlink user-perceived rates, and 5% lower network energy consumption over the predecessors. To sum up, the MetaAAU achieves optimal network performance and energy efficiency.
5G in three years in China has expanded in numbers of users and the coverage area. Now, the users are seeing the fast 5G network available in scenic spots, towns, and rural areas. The use cases have also furthered. HD live broadcasts, and direct photoshoots via social media apps are helping villagers sell their products online. 5G is reducing the digital divide more capably than the 4G network.
In the near future, 5G will be a part of smart agriculture, remote health, and education.
Also read: The State of Digital Divide in Nepal and How to Reduce it?
About the milestone MetaAAU deployment in Beijing?
“Quality first, experience foremost,” said Fan Liqun, head of China Unicom Beijing’s 5G co-construction and sharing work team. “For years we have been committed to building a world-leading, experience-centric 5G network. We are amazed at how well MetaAAU is performing at the more than 1,000 sites on the commercial network, cementing its place in our digital village strategy. This achievement marks a key milestone in our 5G Capital project and is a testament to our constant efforts for a ubiquitous high-quality 5G network. Specifically, we explore various scenarios based on high bandwidth and iteratively adopt innovative Massive MIMO technologies to ensure the best possible 5G and digital experience to our customers.”
Read our post: 4G vs. 5G: Differences Between Two Mobile Networks
Ritchie Peng, President of Huawei 5G Product Line, said, “MetaAAU is one of our major innovative products in 2021. With MetaAAU, we achieve great breakthroughs in network performance and energy efficiency, and this is attributed to our strong investment and continuous innovation in Massive MIMO. We are glad to cooperate with China Unicom Beijing on the thousand-site MetaAAU project and proud to see that MetaAAU achieves the desired performance across the entire network. We believe this can provide a useful reference for global operators in selecting Massive MIMO technologies for different scenarios.”
These scenarios require gigabit networks similar to those for urban areas, but at a lower carbon footprint.