After much anticipation, WiFi 7 was finally announced as WiFi Alliance introduced its WiFi-Certified 7 program. It’s the seventh-generation WiFi standard and the successor to the WiFi 6 or WiFi 6E which promises a blistering speed of up to 46 Gbps, tri-band support, 320 MHz channel, improved latency, and unleash new use cases.
While writing this post, it’s also coming out that WiFi Alliance has started certifying WiFi 7 devices and the technology will be formally ratified in late 2024 but still, it is quite an extraordinary development. Here in this post, we will talk about the major features of WiFi 7, its speed capacity, and its advantages. Below, we explore in detail all the major WiFi 7 features in this tell-all post.
What is WiFi 7?
WiFi 7 is the next evolution in WiFi technology with humongous wireless capacity in data rate and connectivity. It’s basically a new standard in wireless communication technology and is identified as IEEE 802.11be standard. WiFi 7 is also called Extremely High Throughput. This advanced technology will also work in tandem with the 5G and 6G to revolutionize digital communication around the world.
WiFi 7 succeeds WiFi 6E standard released in 2019 and will expectedly revolutionize wireless communication. It will unleash feasibility in meta verse, cloud gaming, 8K content consumption, etc.
WiFi 7 benefits
While speed is the obvious advanced, here are the most noteworthy of WiFi 7 benefits:
- Up to 46 Gbps of speed
- Simultaneous connection on multiple bands
- 320 Mhz wide channel means more bandwidth, efficient network performance
- 4K QAM, OFDMA
- Tri-band support
- Low latency
Where does WiFi 7 stand in wireless communication standards?
WiFi or interchangeably IEEE 802.11 has evolved through the years, and we have to go back to 1999 when the first generation of WiFi was concocted. If you were unaware, each WiFi generation is identified with IEEE 802.11 followed by a a letter or two. The first generation of WiFi came out in 1999 and was called WiFi 2 with its technical title assigned as 802.11a. It worked on a 5 GHz band.
In the same year, the next variant was developed which supported 2.4 GHz. It was called WiFi 1 as it was considered a proper mode of evolution. Technically, it was called 802.11b. The next substantial leap came in 2009 when WiFi 4 was launched with 600 Mbps data capacity. It was called 802.11n. Noticeably, it supported both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands which continues to this day.
In 2024, WiFi 5 (802.11ac) was released with support of up to 1.3 Gbps transmission rate. The successor WiFi 6 was released in 2019 which brought 9.7 Gbps speed. Further improving the standard, WiFi 6E came out the following year in 2020 but with the capability of functioning in the 6 GHz band too. This tri-band support continues in WiFi 7 which is also called 802.11be. The concept for WiFi 7 was substantiated further around 2020 and is headed for a wider launch of compatible devices in 2024.
WiFi 7 is the culmination of extraordinary efforts of the past 25 years made to improve wireless communication.
Evolution of WiFi standards: From WiFi 1 to WiFi 7
| IEEE Standard | Year | Frequency | Data capacity | Regular names |
| 802.11a | 1999 | 5 GHz | 54 Mbps | WiFi 2 |
| 802.11b | 1999 | 2.4 GHz | 11 Mbps | WiFi 1 |
| 802.11g | 2003 | 2.4 GHz | 54 Mbps | WiFi 3 |
| 802.11n | 2009 | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | 600 Mbps | WiFi 4 |
| 802.11ac | 2014 | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | 1.3 Gbps | WiFi 5 |
| 802.11ax | 2019 | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | 9.7 Gbps | WiFi 6 |
| 802.11ax | 2020 | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz & 6 GHz | 9.7 Gbps | WiFi 6E |
| 802.11be | 2024 | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz & 6 GHz | 30 Gbps | WiFi 7 |
Best WiFi 7 features
What makes WiFi 7 so remarkable is its sheer capacity of throughput. It’s said that WiFi 7 can deliver up to 46 Gbps of maximum speed. Think of how much you can do over the internet with that sort of speed, although the real-world speed will differ. But that doesn’t take away anything from what an engineering marvel it will be.
WiFi 7 comes with 320 MHz transmission channels, 4K-QAM support, multi-link operation (MLO), and more. WiFi 7 is backward compatible meaning this standard will support WiFi of previous generations. For more clarity, if you have a smartphone with WiFi 7 compatibility, it will also connect to the internet that complies with WiFi 6 wireless communication standards.
320 MHz bandwidth
WiFi bands work in small bands of 20/40/80/160MHz MHz. WiFi 7 doubles it to 320 Mhz bandwidth. It’s one of the strongest points of this blazing-fast WiFi technology. Thanks to the wider bandwidth channel, WiFi 7 can deliver exponential data rates that can surpass even 40 Gbps much more than what’s possible with 80 MHz, or 180 MHz. To make one comparison, WiFi 7 has 4 times more bandwidth capacity than WiFi 6E. A wider channel allows more data to travel at a faster rate. Thanks to the 6 GHz band, the network faces extremely low interruptions so the capacity and efficiency of WiFi 7 is going to be extraordinary.
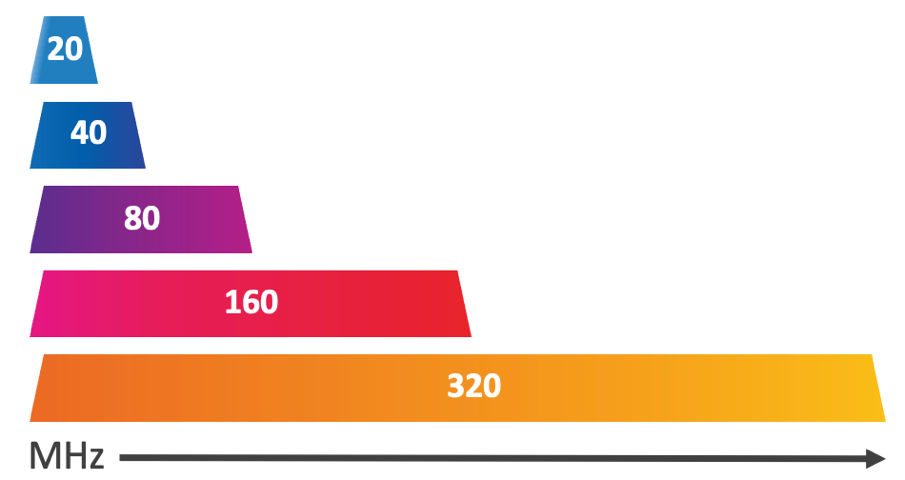
5 GHz band was 160 MHz wide, but, with the new spectrum in the 6 GHz band, that’s increasing to a channel bandwidth of 320 MHz wide. For reference, the entire 2.4 GHz band is only 83 MHz wide, so this is a huge increase. It gives each device a huge speed increment and flexible connectivity.
A normal user may not notice much credible difference with this. However, for those who would consume 8K video content, download and upload extremely large files, and do cloud computing, a seriously fast and capable network would be important and that will be complemented handsomely by the 320 MHz channel.
Bafflingly High Speed
In sum, WiFi 7 is going to be more about speed than anything else. Forget WiFi 5 or even WiFi 6, WiFi 7 delivers the theoretical download capacity of up to 46 Gbps. The end-user will possibly not get this immensely huge broadband speed as it requires compatible devices with all the right components inside. However, the real-world speed will still be huge enough to make use of next-generation use cases feasible.
The world is moving towards AR, and VR, 4K/8K consumption is becoming more common, cloud computing and AI are getting bigger and better, and the world of Large Language Models and (LLMs)-powered chatbots (ChatGPT, Google Gemini) dominating the internet. WiFi 7’s hypnotically fast data rate will improve user experience while online gaming will also improve drastically thanks to low latency. For these to be available, you will need WiFi 7-compatible devices. So far, there are no smartphones that support it, however, companies might bring them later in 2024 or 2025. The bottom line is due to its ostensibly high-speed, WiFi 7 is also called Extremely High Throughput (EHT) network.
Check out: How to Check Internet Speed on your PC or Mobile?
Tri-Band Support
WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 supported dual band connection. WiFi 7 supports tri-band (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) continuing from WiFi 6E. With this feature, the user can connect to either of the band and unleash the performance depending on the feasibility. The 2.4 GHz band gives exceptional coverage with limited speed, however, the 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands offer huge speed bumps. Additionally, WiFi 7 can work on two bands concurrently. This band aggregation means devices can have more flexibility in data transmission while boasting immense speed.
You may want to read: 4 Reasons You Should Upgrade to a Dual-Band Router
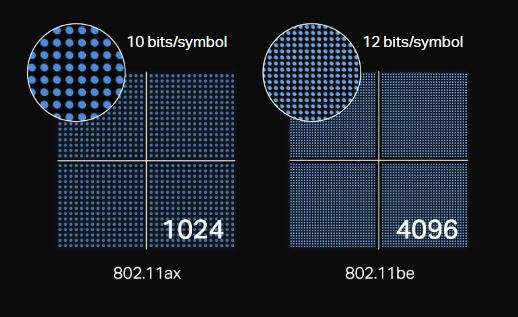
4K QAM Modulation
One of the highlighting features of WiFi 7 is its ability to support 4K QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation). This advanced technology is used to encode bits through the air to the other end. Since there are 4,096 data points in “four quadrants” where the data is to be encoded, the rate of successful data transmission rapidly grows. To compare, WiFi 6 uses 1024-QAM. This is why a WiFi 6 can provide a potential speed of 9.6 Gbps while a WiFi 7 network can unleash up to 46 Gbps juggernaut. The 4096 QAM is a remarkable leap in wireless communication compared to other previous standards.
Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO): 16 Spatial Streams
WiFi 7 attributes its huge throughput capacity to the support for 16 spatial streams, double that of WiFi 6. The streams are what devices use to send and receive information in different directions and exchange the data simultaneously for different devices. In wireless transmission, more spatial streams are better as they facilitate faster data delivery and lower latency.
The increase in the number of antennas and spatial multiplexing gives devices enough bandwidth for smooth connection. The higher number of streams equates to faster speeds it also means more data can be sent and received from devices. So, a WiFi 7 router will essentially provide faster speed, reliability, and consistency in terms of internet performance. Due to this feature, the next-generation WiFi standard will have more available bandwidth and less network congestion meaning data will flow with less interruption.
Multi-Link Operation & Low Latency
If you are using a WiFi 5 or WiFi 6 router, it can connect to one of the bands between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz for data transmission because that’s the ability the standard allows them. As you know, 2.4 GHz is vulnerable to network congestion and its speed can be badly affected while the 5 GHz band gives a big speed bump but offers less coverage. WiFi 7 compatible devices can connect on two bands among the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands thanks to Multi-Link Operation (MLO) technology. This unlocks faster connection through aggregation. It also allows for extremely low latency.
OFDMA
OFDMA or Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access splits available channels into different resource units (RU). This lets the network deliver smaller data packets to multiple users concurrently. This technology helps reduce latency elevate the efficiency of data transmission and make effective use of available spectrum.
OFDMA is not meant to improve faster data rate. But it helps make stable connections for a network. As multiple devices connect to the same WiFi network at the same time, the contest to connect is reduced. This means the network becomes more stable.
Target wake time (TWT)
Conventionally, devices send data when they have something. This increases the wake-up frequency and increases power consumption. Thankfully, the WiFi 7 standard introduced Target Wake Time (TWT) which allows devices to communicate their data transmission needs more efficiently thus lowering power usage. This not only calms the electricity bills but also improves the overall battery life of devices. The feature is very useful for devices that are forever connected to a network and is always in need of sending data such as IoT, and smart home devices. Don’t miss: Internet of Things (IoT) Technologies, Use cases in Nepal
Should you buy a WiFi 7 router?
It’s no doubt that WiFi 7 is the inevitable future and spending money on a WiFi 7 router or a device will be a future-proof investment. And even if you don’t want it, the future next-generation devices will have you get it even without you consciously wanting, smartphones although that’s not happening for a few months at least.
Additionally, iPhone 16, Samsung’s Galaxy S24 Ultra, Z Fold6, and Flip6 come with WiFi 7 support. In fact, most flagship phones these days including the likes of Xiaomi 14, and OnePlus 12 come with the next-generation WiFi connectivity options.

Also, the most modern-day laptops such as the recently launched Asus Vivobook S15 feature WiFI 7 support.
WiFi 7 is Available in Nepal, But Technically
Yes, WiFi 7 is already available in Nepal but that can get tricky. Technically speaking, this technology is with us via the flagship phones we mentioned earlier. However, to enjoy the speed we need compatible routers. That leads us to a sad awakening of its practical reality. WiFi 7 is there but you can’t use it.
That is because the WiFi 7 router is not available in Nepal. So far, internet service providers (ISPs) provide their FTTH fiber internet with up to WiFi 6 support so a leap to WiFi 7 is years behind. Mostly, WiFi 5 (dual-band) routers are available in Nepal. But importing one from abroad is not impossible. But still, it’s rewarding to have something in its most advanced form if possible as it also brings forth many other new features and capabilities.
Also read: NTA’s Minimum Specs Standard for WiFi Routers, Details
Who needs a WiFi 7 router?
Most current-days users have either dual-band 5 GHz or WiFi 6 routers and they do the job as well. However, the need for faster data and minimal latency continues to grow with new use cases. As tech and innovation expand, more improved WiFi will be in demand. That’s when WiFi 7 will find its relevancy. Technicians, large enterprises, heavy and hardcore gamers, and big tech firms will all make use of the next-gen WiFi system due to its cutting-edge features.
At the same time, regular users who are content with whatever their devices have to offer will also end up with WiFi 7 devices in the future. The upcoming generation of flagship phones will have WiFi 7. As it stands, the ecosystem for WiFi 7 will grow over time while those who require continuous fast internet speed, with exceptional network efficiency and reliability will eventually seek WiFi 7. Companies like Netgear, and TP-Link have already launched WiFi 7 routers which come with the most mentioned features in this post. However, they will take time to hit the markets globally.

WiFi routers launched at CES 2024
One of the pioneers of WiFi 7 products, TP-Link announced two WiFi 7 network adapters- an Archer TBE550E and an Archer TBE400UH BE6500 USB card. The former comes with Bluetooth 5.4 and uses PCIe to add WiFi 7 to any desktop computer. The device comes with 320 MHz support and can deliver up to 5.7 Gbps speed. The latter features a 2×2 160 MHz support and can deliver theoretical speed of 2.8 Gbps. These cards are compatible with all Windows 11 computers.
TP-Link also launched next-generation WiFi 7 routers- Archer GE800, BE19000 Tri-Band Wi-Fi 7 Gaming routers. The GE800 router supports a tri-band connection and delivers up to 19 Gbps speed. Expect lightning-fast connection for 8K consumption, as well as cloud-based activities and lag-free high-octane gaming with it. In total, TP-Link displayed 6 WiFi 7 routers at the CES 2024 event.

Likewise, Asus unveiled WiFi 7 Mesh Routers namely ZenWiFi BQ16 and BQ16 Pro at CES 2024. The next-generation routers come with speed support of up to 30 Gbps and 8000 sq. ft. coverage for smart homes. Users who are into gaming and 4K HDR entertainment will also find themselves at home with these two extraordinary hardware.

WiFi 7 is a future-proof tech rather than a current need!
To be fair, there is no true answer to this question. The world already has WiFi 6E which comes with incredible data transmission prowess over WiFi 5 and WiFi 6. And just like with 5G, there doesn’t seem to be the real need for the next-gen WiFi connection. However, technology only keeps improving and researchers and engineers won’t stay complacent with current technology.
Anyway, the world is moving towards metaverse, artificial intelligence, extended reality (XR), 8K multimedia consumption, virtual reality (VR), cloud gaming, and the need for extremely high-quality internet, and not just the speed bump is required. Simultaneous connectivity with uniform network capacity, low latency, and faster server response will form the key to digital communications in the immediate future. That’s where WiFi 7 will find its truest justification. And to the normal user, it’s always cool to have something the most recent, advanced, and the most capable.
Check out: How to improve your home internet speed?
When will WiFi 7 come out?
WiFi 7 could officially get its birth towards the end of 2024. Qualcomm, Samsung, OnePlus, and MediaTek have already brought an array of WiFi 7 products. In the latest development, WiFi Alliance has begun certifying WiFi 7-compatible devices. So, expect more of such devices soon. 2024 continues to remain a key year for WiFi 7.
Which WiFi 7 feature stands out for you? How frustrating is it to you that you can buy a device with WiFi 7 support, but still can’t use its speed? Do share your opinion with us in the comment section below.